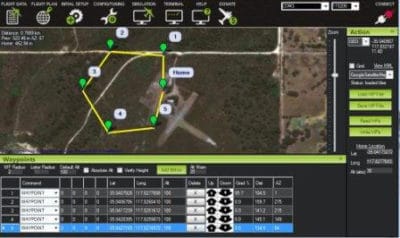
Drone Waypoint GPS Navigation is advanced technology. It is very useful both today and even more so into the future as drones take on new functions and roles in business and other areas.
Waypoint GPS Navigation allows a drone to fly on its own with it’s flying destination or points preplanned and configured into the drone remote control navigational software.
This instructs the drone where to fly; at what height; the speed to fly at and it can also be configured to hover at each waypoint. It is a route and destination planner for your drone.
At the bottom of this article, I have a few nice videos which explain GPS waypoints, how waypoints are being used and also how to setup waypoints on a drone. So if you want to skip all the reading and go straight to the videos, then please feel free to do so.
I sure hope the information in this article and videos will be helpful to you. I love the explanation of GPS Waypoints in the first video by Lyle Brotherton. He uses crunchy bars for waypoints. Excellent.
To see how easy it is to setup waypoints on a drone and see it flying the route, watch this DJI Phantom Waypoint tutorial.
Understanding Waypoints On A Map Or GPS Device
Let’s start at the beginning and describe what exactly a waypoint is. Satellite Navigational devices function around one premise and that is that they can mark a location anywhere on the earth. The term that we use for that is a “Waypoint” and the dictionary definition is that it is a reference point in physical space.
Before GPS devices we would have to take a map and open the map. We would have to visually look at the map and find the location that we’re at or find the location that we want to move to and mark it with a pen. That’s exactly the same with a GPS satnav. The points are stored electronically rather than on the map as a pen mark.
There are 3 important things we can do with GPS waypoints which takes it beyond the realms of a mark of the map.
1) From anywhere around the world, whether that’s 20 meters away from here or 50 meters, 100 kilometers or 1,000 kilometers, we can come straight back from our starting point, an exact location in a straight line from anywhere.
2) Waypoints can be transferred onto a computer’s digital mapping software.
3) We can share our waypoints with other people.
The below video explains waypoint navigation in a very easy to understand way.
GPS Waypoint Uses
Present Waypoint Uses Outside of Drones
- Mountaineers and hikers use Satnavs along with old style compass and maps.
- Couriers, delivery persons and taxi drivers both in cities and countryside program in their delivery address waypoints and the satnav finds the routes to these points.
- Resourceful tourists will program waypoints into their handheld satnav all the points of interest they want to visit along with accommodation and restaurants.
Drone GPS Waypoint Uses
Engineering Project Site Surveys: When waypoints are programmed into the application, the drone can go directly to the first point and proceed to each point in turn, filming or taking photos of each point. Presently being used to film and photo: Solar Farms (See video below), Pipe lines, Railway Tracks, Telecoms Masts and Archaeology sites.
Environment & Conservation: Surveying areas of interest whether coastal erosion to areas affected by illegal dumping of waste.
Agriculture: Surveys of farm buildings and fencing, which is presently being used. Used to search for missing sheep in hills and mountains areas. Agricultural drones use advanced thermal vision cameras and multispectral sensors along with specialized software which give farmers new ways to increase analyse farm date to yields and reduce crop damage.
Parcel Delivery: This is perhaps somewhere in the future with a lot of problems to overcome. Programmed GPS waypoints would map the route from the delivery drone. The delivery drone can take a number of parcels and go from delivery point to the next without the need for a pilot.
However, drones have to overcome many other problems such as obstacle avoidance and be practically 100% safe. Drones are noisy so they would have pretty quiet. Drone flight times are short averaging around 15 to 20 minutes of flight. There is also rules and regulations to flying drones which may result in parcel delivery drones never making it to the market.
Ad: Check out this superb DJI Mavic 2 Pro deal on Amazon.
There are many companies looking to use drones to delivery parcels. Amazon receives a lot of news. The French Postal service is researching parcel delivery and Netherlands based Aerialtronics had an inquiry about using drones to delivery diamonds in the city of Antwerp.
We may see drone parcel deliveries within large campus or in large private business such as pharmaceuticals and mining first and it may be several years if at all before the Amazon drone coming knocking on your door. You can read further on the projects and the latest news on drones delivering parcels here.
There really are so many applications for drones. In the next video we see how a Chinese company use DJI Phantom 2 drones to survey their extensive solar farm.
Advanced Waypoint GPS Navigation Technology In Drones
Drone waypoint GPS Navigation is far more advanced than in a handheld GPS device. It has to fly the drone, keep it very stable in the air, fly to the configured waypoints coordinates, altitude and speed. It then has to come back to it’s starting point. Some drone waypoint software is so advanced that up to 500 waypoints can be programmed in.
At any stage during the waypoint flight the pilot on the ground can take back control of the drone.
Uses For Drone Waypoint GPS Navigation Technology
Drones are being used more and more in all types of site surveys from building construction, railway and road maintenance, power stations, dams, archaeology sites and environmental surveys. They are also being used by insurance companies for viewing damage to buildings. Drones are also being used in agriculture to inspect crops, fencing, glasshouses and even find missing cattle and sheep.
 With Waypoint GPS navigation, a site can be surveyed at the correct locations. The drone can fly directly to each specified location while the pilot on the ground concentrates on operating the camera to take aerial photographs of video. The drone takes the shortest route to each waypoint saving battery and filming time.
With Waypoint GPS navigation, a site can be surveyed at the correct locations. The drone can fly directly to each specified location while the pilot on the ground concentrates on operating the camera to take aerial photographs of video. The drone takes the shortest route to each waypoint saving battery and filming time.
Without waypoint GPS navigation, aerial 3D photogrammetry and lidar imaging would require a two person setup. To create a 3D map of a land mass from aerial photos, a camera is mounted on a drone or aircraft and is pointed vertically towards the ground. To create a 3D models of a monument, statue or even a face, the camera is mounted horizontally.
The drone camera will capture hundreds, even thousands of overlapping photos of the ground, structure or model. The photos will overlap each other, by 80 to 90%. The 3D map or 3D model is then created using aerial image stitching 3D mapping photogrammetry software.
The drone will fly using autonomous waypoints. To overlap photos of an object or land mass by 80 to 90% would be impossible to complete accurately by pilot navigation. Each photo captured will also have it’s GPS coordinates (Geotagging) saved, which also assists to build the 3D map. A geotagged photograph is associated with a geographical location.
The advancement of drones to deliver parcels will very much require even more advanced waypoint technology. The costs of having a pilot for every drone delivering parcels would be expensive. But if drones are pre-configured with their destination waypoints to deliver parcels, they can go straight to the location and then to the next location taking the shortest route possible.
Drones flying about all over the country and cities with parcels is not so much science fiction any more. But is it something that people want. There are big technology companies behind the use of waypoint GPS technology in parcel delivery systems. Google have a program for home delivery called Project Wing. Amazon are also working on their parcel delivery system.
What we may see is companies, which have large physical sites and many buildings use drones with waypoint technology to deliver parcels and mail within their grounds as well as site surveys.
Drones And Companies With Waypoint GPS Navigation Products
Ace 2 from DJI – This allows for precise flight positioning, high mobility and ease of use. With their advanced professional ground station system, their unmanned drones become a fully automated aerial work platform, with applications in specialized professions, including various industrial operations.
Note From DJI About A2: On December 12, 2015, Google stopped supporting Google Earth. Since DJI’s PC Ground Station software is based on the Google Earth API, we will also discontinue support for PC Ground Station. As a result, DJI’s Ace One WP flight controller and 900M Datalink, both of which rely on our PC Ground Station software, will also cease to be functional. The 2.4 GHz Bluetooth Datalink’s PC Ground Station functionality will also cease to be functional, however the iPad Ground Station functions will not be affected.
Ace 3 From DJI – Groundstation can be realized in DJI GO APP With Lightbridge 2, and in PC Ground Station with Lightbridge 2 or DATALINK PRO. The A3 is equipped with 3 IMU units and 3 GNSS with additional analytical redundancies for a total of 6 redundancies.
ArkBird Autopilot: This System is an all-in-one solution for your FPV model’s navigation. This unit is loaded with features such as GPS waypoint flight, ‘Return to Home’ functionality, auto-leveling, altitude hold and a lot more. It also utilizes GPS, barometer and attitude sensors to stabilize/control your model’s flight.
Spreading Wings S1000+: This professional drone from DJI has Waypoint technology inbuilt with a choice of either the Ace Waypoint or the Wookong-M Waypoint. The Wookong M Waypoint has many features including waypoints along with flight stabilization. With the Spreading Wings, there is a big choice of gimbals for many top quality cameras.
Phantom 4 Pro V2.0 from DJI has waypoint navigation plus many more intelligent flight modes including 5 directions of collision avoidance.
Phantom 3 and Inspire 1 from DJI also have waypoint navigation. The waypoint hardware was already in these quadcopters and the firmware / application update in September 2015 added the waypoint features.
Scout X4 from Walkera Technology allows you to program 128 waypoints using it’s Ground Station system. The Voyager 3 professional aerial filming drone also uses the same Ground Station system. Walkera drones are packed with innovation and features.
Multirotor G4 by Service-Drone – This German company produces top of the range drones along with a business model where you can become a partner or distributor. The G4 multirotor has a unique GPS flight assistance for manual or fully autonomous flying and it allows you to set waypoints before or during the flight. Fly autonomously with planned survey flights. Up to 500 waypoints can be configured on the G4.
Altura Zenith from Aerialtronics – Uses the Altura GCS Application to manage both autonomous navigation and manual flights. Pilots have the option of flying via waypoints of make repetitive flight patterns.
APM Copter from Ardupilot – APM:Copter has a full range of flight capabilities from fast paced FPV racing to smooth aerial photography to fully autonomous complex missions which can be programmed through one of 4 elegant and well-developed software ground stations. The entire package is designed to be safe, feature rich, open-ended for custom applications and increasingly easy to use even for novice users.
X8 Quadcopters from 3DR. This beautiful drone uses the Pixhawk v2.4.5 Autopilot hardware to automate and create repeatable flight paths, to gather data beyond the visible spectrum. It can generate point clouds for precision survey. The X8 can use both Mission Planner or APM Planner Software 2.0 for drone GPS waypoint navigation. This is the same as the APM Copter above. This fantastic X8 models from 3DR are no longer being manufactured.
MicroPilot – Develops, innovates and supplies Autopilot hardware and software to over 850 clients in 70 countries. They are a World Leader in Professional UAS Autopilots.
Geodedics – design and supply precise Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) solutions to address a wide range of requirements for Air, Sea and Land, including high speed pointing/attitude and relative position/angle applications.
Waypoint GPS navigation is not on every drone or quadcopter. However as technology advances and competition increases, waypoint hardware along with the waypoint planning software will become available in nearly all drones coming onto the market.
I’ll finish off this article on autonomous drone flying using GPS waypoints with a couple of videos. This first shows you how Waypoints is setup on both the DJI Phantom 3 and Phantom 4 drones.
This video shows you waypoints on the older Phantom 2 and discussed waypoints a bit further.